Module 3.0: Pro Tips and Tricks
Getting the Most Out of Large Language and Generative Models: A Guide for Data GovCon Professionals
I. How to Get Good at This
The future of work is going to be powered by artificial intelligence (AI). Whether you're using ChatGPT Office 365 Copilot or any of the numerous AI-powered tools coming down the pike, you should start looking for the shortcuts, pro tips and life hacks to keep your lead on your professional competition. To stay ahead, you must not only understand these models but also become adept at using them. How? By grasping the basics of their design, operation, and application. This means delving into an array of manuals and instructions, deciphering jargon-laden terms, and seeking out quality walkthroughs and guides.
II. Read Manuals and Instructions
Every AI model, whether it's GPT-4 or BARD, comes with a manual or set of instructions. These documents are essential for understanding how to properly use and leverage the model’s capabilities. Often, they contain valuable information about the model’s structure, function, and operation.
So how can you efficiently navigate through these manuals and instructions? First, start by identifying the key sections that are most relevant to your needs. This could be sections on training the model, adjusting its parameters, or testing its performance. Next, create a summary or cheat sheet of the most important points from each section for easy reference. Bookmarking or highlighting key pages can also be helpful.
Remember, these manuals are written by the creators of the model. They contain insights that you simply won’t find elsewhere. So while they may seem daunting at first glance, they are well worth the time and effort.
III. Understanding Jargon-laden Terms
Working with large language and generative models often means dealing with an array of complex and jargon-laden terms. It seems like data scientist dumbed these terms straight out of the lab without any translation for us common folk. These terms can seem impenetrable at first, but understanding them is crucial for effectively using these models.
Here are a few examples:
- Transfer learning: This term refers to the practice of using pre-trained models on new tasks. The idea is to leverage the knowledge gained from one task to improve performance on another.
- Tokenization: This is the process of breaking down text into smaller units (tokens) such as words or phrases. It is a fundamental step in many language processing tasks.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These are AI models that use two neural networks – a generator and a discriminator – to produce new, synthetic instances of data that can pass for real data.
There are a few excellent glossaries out there, though most of them still seem to cater to the highly technical folks. This one by Product Hunt has a convenient layout that include definitions for "16-year-old".
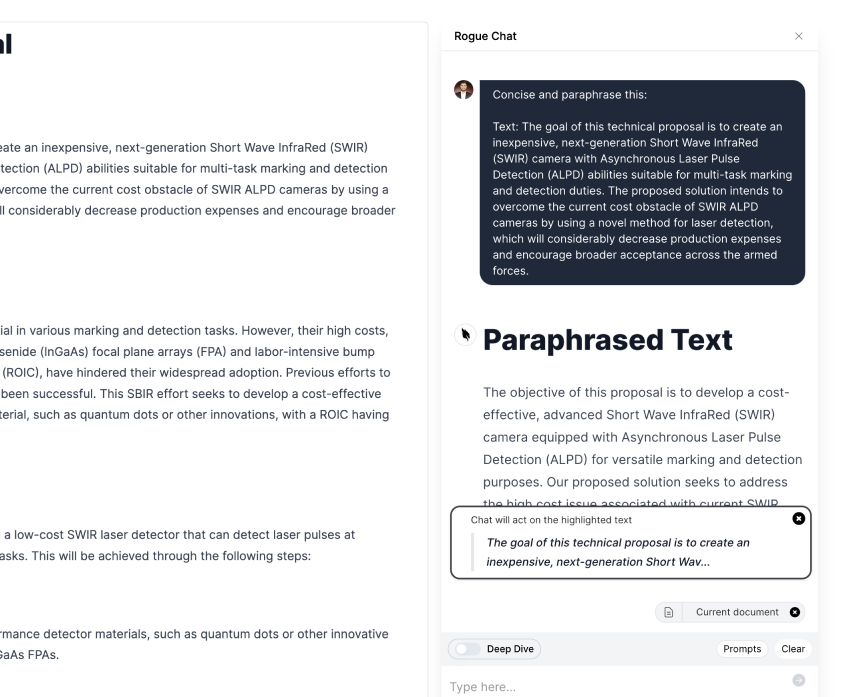
You can copy this hack by using AI (using AI to explain AI is a nerdy irony), check it out:
IV. Finding Walkthroughs and Guides
Even with manuals and instructions at hand, sometimes it helps to see these models in action. That's where walkthroughs and guides come in.
Quality walkthroughs and guides can be found on various platforms such as GitHub repositories, AI-focused blogs like Towards Data Science, or forums like Medium and Reddit’s r/MachineLearning subreddit. YouTube is another excellent resource for video tutorials.
Remember that not all guides are created equal, so find some authors that you like and whom you think provide quality information, and bookmark them.
V. Next Level
Understanding large language and generative models isn't just beneficial - it's necessary for any data science professional looking to excel in their field. The more you know about these models, the better equipped you will be to leverage their capabilities effectively.
Don’t stop at reading this guide – go beyond! Explore different models, dive deeper into their mechanics, play around with their parameters. Remember that learning is a continuous process, especially in a rapidly evolving field like AI.
Getting the most out of large language and generative models requires patience, practice, and a willingness to delve into complex materials. It might seem overwhelming at first, but with time and effort, you'll find yourself becoming more comfortable - even adept - at navigating this exciting landscape.
VI. Practical Exercise
Take a few of the more arcane sounding terms from the list below and try the GPT translator hack from section 3 above.
Glossary of Terms for Mortals Courtesy of The New York Times
Anthropomorphism: The tendency for people to attribute humanlike qualities or characteristics to an A.I. chatbot. For example, you may assume it is kind or cruel based on its answers, even though it is not capable of having emotions, or you may believe the A.I. is sentient because it is very good at mimicking human language.
Bias: A type of error that can occur in a large language model if its output is skewed by the model’s training data. For example, a model may associate specific traits or professions with a certain race or gender, leading to inaccurate predictions and offensive responses.
Emergent behavior: Unexpected or unintended abilities in a large language model, enabled by the model’s learning patterns and rules from its training data. For example, models that are trained on programming and coding sites can write new code. Other examples include creative abilities like composing poetry, music and fictional stories.
Generative A.I.: Technology that creates content — including text, images, video and computer code — by identifying patterns in large quantities of training data, and then creating original material that has similar characteristics. Examples include ChatGPT for text and DALL-E and Midjourney for images.
Hallucination: A well-known phenomenon in large language models, in which the system provides an answer that is factually incorrect, irrelevant or nonsensical, because of limitations in its training data and architecture.
Large language model: A type of neural network that learns skills — including generating prose, conducting conversations and writing computer code — by analyzing vast amounts of text from across the internet. The basic function is to predict the next word in a sequence, but these models have surprised experts by learning new abilities.
Natural language processing: Techniques used by large language models to understand and generate human language, including text classification and sentiment analysis. These methods often use a combination of machine learning algorithms, statistical models and linguistic rules.
Neural network: A mathematical system, modeled on the human brain, that learns skills by finding statistical patterns in data. It consists of layers of artificial neurons: The first layer receives the input data, and the last layer outputs the results. Even the experts who create neural networks don’t always understand what happens in between.
Parameters: Numerical values that define a large language model’s structure and behavior, like clues that help it guess what words come next. Systems like GPT-4 are thought to have hundreds of billions of parameters.
Reinforcement learning: A technique that teaches an A.I. model to find the best result by trial and error, receiving rewards or punishments from an algorithm based on its results. This system can be enhanced by humans giving feedback on its performance, in the form of ratings, corrections and suggestions.
Transformer model: A neural network architecture useful for understanding language that does not have to analyze words one at a time but can look at an entire sentence at once. This was an A.I. breakthrough, because it enabled models to understand context and long-term dependencies in language. Transformers use a technique called self-attention, which allows the model to focus on the particular words that are important in understanding the meaning of a sentence.
Share it in the group. We're excited to see what you come up with!
GovCon GPT Masterclass
31 lessons
Sign up for Rogue today!
Get started with Rogue and experience the best proposal writing tool in the industry.