Module 1.b: Your GPT Junior Writing Assistant
©️You are free to adapt and reuse provided (1) that you provide attribution and link to the original work, and (2) you share alike. This course and all of its contents are the property of UseRogue.com and are offered under the Creative Commons BY-SA 4.0 License.
I. Introduction
Imagine having a junior writing assistant who can help you draft texts, generate creative ideas, and even write complete documents. This is how you should think of Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT) and other generative models. These artificial intelligence (AI) models are designed to understand and generate human-like text, making them valuable tools for writers.
But just like a junior writing assistant, these models require a fair amount of coaching and instruction. They are not infallible; their work needs to be checked before it goes to print. Thinking of GPT in this way can save you a lot of trouble and also keep your from expecting more out of the models than they are designed to provide. You wouldn’t give an intern a a report to draft and send their first draft to your customer or boss without reading every line and fixing the errors.
In the GovCon space you need to take particular care; the more niche the subject matter, the less specific the model will be when generating content. The more niche the subject matter, the more context you will have to give it (more on that later in prompt engineering basics).
II. Understanding GPT and Other Generative Models
At their core, GPT, and models like it, are language prediction machines. They analyze a given input and try to predict what comes next. This makes them capable of generating coherent, human-like text.
However, these models do have limitations. They lack understanding of context, nuance, or factual accuracy. They can't independently verify information or distinguish between reliable sources and misinformation. Hence, it's crucial to know what they can do as well as what they can’t.
III. Thinking of GPT as a Junior Writing Assistant
Just like a new hire, GPT needs guidance to perform effectively. While the model is incredibly advanced and can generate impressive text, it doesn't inherently know your writing style, your target audience, or your content preferences. It's important to remember that GPT learns from the data it has been trained on and the instructions it receives from you.
As an AI junior writing assistant, GPT relies on clear direction and feedback in order to provide you with the best possible output. By giving specific instructions and providing examples of what you're looking for, you can help shape its understanding of your unique writing style. This way, GPT can adapt its responses to align more closely with how you would write.
Additionally, understanding your intended audience is key when working with GPT as a junior writing assistant. By clarifying who will be reading your content and what their expectations are, you can guide the model towards generating text that resonates with them. Whether it's using a certain tone or phrasing that appeals to a particular group of readers or adhering to specific guidelines such as formal language in academic settings - these considerations will ensure that GPT produces content suitable for your target audience.
In terms of content preferences, communicating these clearly is essential for maximizing GPT's performance as well. If there are certain topics or themes that should be emphasized or avoided in your writing projects, make sure to convey this information explicitly so that the model understands which directions to prioritize.
IV. You Can't Train It, But You can Guide It
The models are “trained”, you are not going to train them. You are also not going to "tune it", you are going to give the model "context" and "prompts", and this course is going to help you do that better.
📣Wonk note:
Generative models like GPT are trained on large datasets of text, which allows them to learn patterns and generate new text that is similar in style and tone to the data they were trained on. Tuning refers to the process of adjusting the model's parameters or fine-tuning it on a smaller dataset to improve its performance on specific tasks.
Imagine playing a game where one player starts saying a sentence and the other player has to complete the sentence. For instnace:
Player 1: “no sense crying over” Player 2: “spilt milk”
How would you get really good at predicting the end of the sentence? you would read a lot of sentences so you knew what usually comes next, not just in common idioms, but with Shakespeare, news articles, and C++ code.
This is called training, they show the model a lot of examples so the model statistically estimates the next word, sentence, etc.
Now, what if you wanted player 2’s answer to be “spilled milk”
You would tell player two “no it’s spilled milk, not spilt milk”
Now do that on a large scale so it produces Department of Defense jargon instead of Department of State jargon. This is tuning.
You’re not doing either of these things.
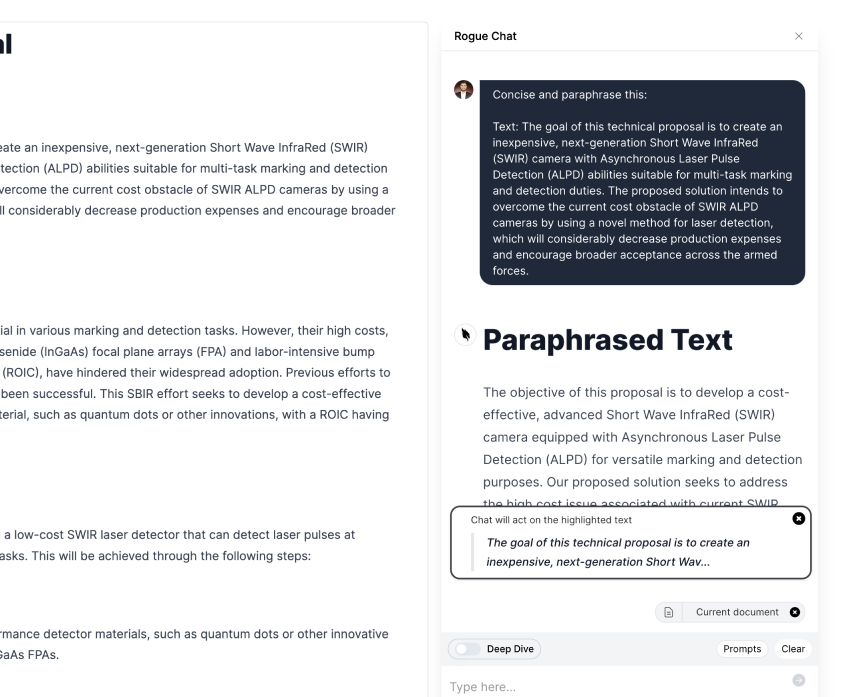
When using GPT as a junior writing assistant, it is important to understand that simply asking the model to generate a company overview statement might not always produce the desired results. While providing some information about your company can be helpful, it is often more effective to provide the model with a detailed prompt that includes context, tone, format, and other specifications.

By giving the model additional guidance through a comprehensive prompt, you can improve its understanding of what you are looking for in a company overview. Including relevant details such as industry-specific terminology or key accomplishments can help the model generate a more accurate and tailored description.
Specifying the desired tone and format can ensure that the output aligns with your intended communication style. Whether you need an informative and professional overview for potential clients or a creative and engaging introduction for marketing materials, clearly defining these parameters will enable the model to deliver content that meets your specific needs.
Additionally, considering other specifications beyond just content may further enhance the quality of generated text. For instance, if you require bullet points or subheadings in your company overview statement, explicitly mentioning these preferences in the prompt will guide the model towards producing structured and organized output.
V. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
One common mistake when using these models is overreliance on their abilities. Without proper supervision and checks, GPT can generate text that is irrelevant or inaccurate. A lot of folks talk about "hallucinations" with GPT models and act as though a model writing about something it is not trained on is somehow appalling. Well, if you had a new writing assistant right out of school and asked them to write something they knew nothing about, and they were over eager and couldn't ask you question, what would it do? It would do the same thing.
More on hallucinations in the next section, bottom line don't be surprised if your model writes something wrong, it just means you didn't give it enough instruction or context.
To avoid these mistakes, always review the output from these models carefully. Ensure that the information is accurate and relevant to your topic. Remember also that while these tools can aid in generating ideas or drafting articles, they cannot replace human creativity and critical thinking.
VI. Maximizing the Use of GPT in Writing
Used responsibly and productively, GPT can greatly enhance your writing process. It can help brainstorm ideas, draft articles quickly, or add creativity to your writing.
To optimize its use, start with detailed instructions for each task and provide regular feedback for improvement. Experiment with different prompts and styles until you find what works best for you.
Successful users of GPT have shared how it has helped them overcome writer's block, increase productivity, or even generate novel ideas for fictional stories.
VII. Trust but Verify
While GPT and other generative models are powerful tools, it's important to remember that they are just that — tools. They require guidance and supervision to function effectively.
Using these models responsibly means understanding their limitations and strengths. It means being prepared to invest time in training and supervising them just like you would with a junior writing assistant.
As AI advances, there's no doubt that tools like GPT will become more sophisticated and integral to the writing process. But no matter how advanced they get, they'll always need the magic ingredient only a human writer can provide — critical thinking.
In conclusion, embrace your AI junior writing assistant but remember: like any good writer, you must check their work before hitting 'publish'.
VIII. Practical Exercise
- head over to Chat.openai.com and set up an account is you haven't yet, if you have an account, login. Stick to the 3.5 model.
- Input this prompt: write a company capabilities statement for a government contract company that does professional services called “Acme Inc.”
- Now input this prompt sequence:
- imagine you are marketing expert (hit “stop generating” if you don't want to see al it’s output)
- your company is called Acme Inc. and provides business, financial, and program management services to the Department of Health and Human Services (hit “stop generating” if you don't want to see al it’s output)
- write a 500-word comprehensive company capabilities statement, focus on explaining the services
- Congratulations, this is called “prompt engineering” and it’s one of the highest paid and most in-demand jobs right now
- Copy the link to your chat and share it in the LI group

6. Give feedback below
GovCon GPT Masterclass
31 lessons
Sign up for Rogue today!
Get started with Rogue and experience the best proposal writing tool in the industry.